by Scott Bronstad | Dec 28, 2022 | Case Study, How To
A programmable device is a piece of hardware that can be programmed to perform a specific set of tasks or functions. These tiny devices are often used in industrial and commercial settings, including manufacturing, healthcare, and automotive, to automate processes and improve efficiency.
There are many different types of programmable devices, including microcontrollers, Programmable logic devices (PLDs), and various Flash devices. Each of these devices has its own unique set of capabilities and is used for different applications.

NXP Kinetis® K02 MCU for Low Power Applications (MK02FN64VLH10)
Microcontrollers (MCU) are small, single-chip computers that are often used in embedded systems, such as sensors, appliances, and automotive systems. They are highly programmable and can be programmed to perform a wide range of tasks, from simple control functions to complex algorithms.
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, a PLD has an undefined function at the time of manufacture. Before the PLD can be used in a circuit it must be programmed to implement the desired function.[1] Compared to fixed logic devices, programmable logic devices simplify the design of complex logic and may offer superior performance. Unlike microprocessors, programming a PLD changes the connections made between the gates in the device.
Another example of a programmable device is a single-board computer (SBC). SBCs are small, single-chip computers that can be programmed to perform a variety of tasks, such as running a web server, controlling a robot, or playing media. Some popular examples of SBCs include the Raspberry Pi and the Arduino.
Programmable devices are also used in the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT devices are connected to the internet and can be programmed to perform a variety of tasks, such as collecting and transmitting data, controlling other devices, and interacting with users. Some examples of IoT devices include smart thermostats, smart locks, and smart appliances.
In summary, programmable devices are used in a wide range of applications, including control systems, automation systems, data acquisition systems, and the Internet of Things. They can be programmed to perform a variety of tasks and are used in industries ranging from manufacturing to home automation.
Examples of Programmable Device Applications
An example of a programmable device is a smart thermostat. These devices can be programmed to automatically adjust the temperature in a home or office based on the preferences of the user. They can also be controlled remotely using a smartphone app, allowing users to adjust the temperature from anywhere.
Programmable Devices for Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, programmable devices include devices such as insulin pumps and pacemakers. Insulin pumps are small, portable devices that deliver a continuous supply of insulin to patients with diabetes. The pumps can be programmed to deliver insulin at specific intervals throughout the day and can be adjusted as needed based on the patient’s blood sugar levels.
Pacemakers are small devices that are implanted in the chest to help regulate a person’s heartbeat. They can be programmed to deliver electrical impulses to the heart when needed, helping to prevent arrhythmias and other heart rhythm disorders.
Robotic surgical systems are another example of programmable devices used in healthcare. These systems allow surgeons to perform complex surgeries using precise robotic instruments, which are controlled by a computer program. The use of robotics in surgery can help to reduce the risk of complications and improve patient outcomes.
Other examples of programmable devices used in healthcare include medical monitoring devices, such as heart rate monitors and blood pressure monitors, and devices that assist with rehabilitation, such as exoskeletons and robotic physical therapy devices. Overall, programmable devices play an important role in healthcare by providing patients with the care and treatment they need to improve their health and quality of life.
Programmable Devices for Automotive
 Programmable devices are also used in the automotive industry, such as in self-driving cars. These cars are equipped with sensors and algorithms that allow them to navigate and make decisions on the road. Some examples of programmable devices used in automotive include:
Programmable devices are also used in the automotive industry, such as in self-driving cars. These cars are equipped with sensors and algorithms that allow them to navigate and make decisions on the road. Some examples of programmable devices used in automotive include:
- Engine control units (ECUs) – ECUs are microprocessors that control various aspects of an engine, including fuel injection, ignition timing, and engine temperature. ECUs are programmed to optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Automatic transmission controllers – Automatic transmission controllers are microprocessors that control the shifting of gears in an automatic transmission. These controllers are programmed to optimize shift points based on various factors such as engine speed and load.
- Electronic stability control (ESC) systems – ESC systems are microprocessors that control the braking and throttle of a vehicle to help maintain stability during sharp turns or sudden changes in direction. These systems are programmed to react to certain stimuli, such as steering angle or yaw rate, to help keep the vehicle on track.
- Adaptive cruise control (ACC) systems – ACC systems are microprocessors that control the speed of a vehicle based on the speed of other vehicles in front of it. These systems are programmed to maintain a safe following distance and adjust the speed of the vehicle accordingly.
- Telematics systems – Telematics systems are microprocessors that transmit and receive data wirelessly, allowing for remote monitoring and control of a vehicle. These systems are programmed to transmit data such as location, speed, and fuel level to a central server, which can then be accessed by the vehicle owner or a fleet manager.
Overall, programmable devices play a crucial role in the automotive industry, helping to improve vehicle performance and safety. These devices are constantly evolving, with new technologies and capabilities being developed all the time.
BPM Makes Programming Devices Easy
BPM has delivered more fine-pitch automated programming systems than all of our competitors combined. BPM programmers and software are the fastest universal programmers in the world, supporting MCUs, FPGA, eMMC, NAND, NOR, Serial Flash memory devices, and more. What really sets them apart is how easy BPM systems are to set up and run, without requiring a skilled operator. To request a demo, please click here.
Device Programmers from BPM | https://www.bpmmicro.com/how-to-program-in-house/ Video: Bring Programming In-House

by Scott Bronstad | Dec 21, 2022 | Announcements, News
According to Global SMT, Samsung announced the world’s first DDR5 DRAM chips manufactured using 12nm semiconductor manufacturing technology. The company unveiled its 16Gb DDR5 DRAM chips and said they have already been evaluated for compatibility with AMD’s Zen processors.
The new chips are more efficient and offer 23% better performance than previous-generation DRAM chips. The South Korean company said it made this technological leap possible by using high-κ material, which increases cell capacitance. Samsung also used its own technology to improve critical circuits.
The company’s new DDR5 DRAM chips use advanced multi-layer lithography to achieve the industry’s highest die density and offer 20% higher wafer productivity. These chips are capable of transfer rates of up to 7.2 Gbps, which is equivalent to processing two 30GB 4K movies in one second.
Samsung will begin mass production of its 12nm class DDR5 DRAM chips in early 2023. Products based on these DRAM chips can be expected sometime in the last quarter of 2023.
DDR5
DDR5 (Double Data Rate 5) is a type of computer memory that is used in computers, servers, and other devices that require high-speed data transfer. It is the successor to DDR4 and offers improved performance and higher density compared to its predecessor.
The size of the technology used to manufacture a memory chip, such as DDR5, is typically measured in nanometers (nm). A smaller technology size generally allows for higher density and better performance, as it allows more transistors to be packed into a smaller area.
As of 2021, DDR5 memory chips are generally manufactured using technology sizes of 10nm or 12nm. Using a 12nm technology size allows for a higher density of transistors on the chip, which can lead to improved performance and power efficiency.
It is worth noting that technology sizes are constantly improving, and memory manufacturers are continually working on new technologies and processes to further improve the performance and density of their products.
Read Global SMT Article
by Scott Bronstad | Dec 21, 2022 | Cybersecurity
Benefits of Cybersecurity
Implementing robust manufacturer cybersecurity measures can provide several benefits for manufacturers. Some of these benefits include:
- Protecting sensitive information: Cybersecurity measures can help protect sensitive information, such as trade secrets, intellectual property, and customer data, from being accessed or stolen by unauthorized individuals or organizations. Modern manufacturers often handle sensitive information such as intellectual property, trade secrets, and customer data. Cybersecurity measures can help protect this information from being accessed by unauthorized individuals or organizations.
- Maintaining customer trust: A breach of cybersecurity can lead to the loss of consumer trust and damage to a company’s reputation. End users expect their personal and financial information to be protected when doing business with a manufacturer. By implementing strong cybersecurity measures, manufacturers can maintain customer trust and reduce the risk of damaging their reputations.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: Many industries have specific cybersecurity regulations that must be met. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, manufacturers can ensure compliance with these regulations and avoid potential fines or other consequences.
- Avoiding financial losses: Cyberattacks can result in significant financial losses for manufacturers. These losses can come from the cost of responding to the attack, as well as lost revenue and profits due to disrupted operations. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures can help prevent these losses.
- Ensuring operational continuity: Cyberattacks can disrupt manufacturing operations, leading to delays and other issues. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, manufacturers can ensure that their operations continue smoothly and without interruption.
- Improving operational efficiency: Cybersecurity breaches can disrupt manufacturing operations, leading to lost productivity and revenue. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures can help prevent these disruptions and improve operational efficiency.
- Reducing financial risk: Cybersecurity breaches can result in significant financial losses, including the cost of responding to the breach, damages to reputation, and legal fees. Implementing strong cybersecurity measures can help reduce the risk of these financial losses.
Implementing Manufacturer Cybersecurity
- Conduct a cybersecurity risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats to your manufacturing operations. This should include evaluating the security of your network infrastructure, identifying any weak passwords or lack of multi-factor authentication, and assessing the security of your connected devices and systems.
- Implement strong password policies and ensure that all employees are using unique, complex passwords for all accounts and systems. Consider implementing multi-factor authentication for added security.
- Regularly update and patch all software and systems to ensure that any known vulnerabilities are addressed.
- Implement network segmentation to limit the spread of any potential cyber threats and isolate sensitive data from non-sensitive areas.
- Implement a firewall and intrusion detection/prevention systems to monitor and protect against potential cyber threats.
- Regularly train employees on cybersecurity best practices and make sure they are aware of the potential risks and how to identify and report potential threats.
- Implement a security incident response plan to have a clear process in place for handling any potential cyber threats.
Many BPM users operate in a strict no-internet connection environment. This is a crude yet highly effective security measure.
Due to the rapid changes in threats and the general ignorance of best practices, you should seriously consider working with a cybersecurity expert or consulting firm to ensure that your manufacturing operations are adequately protected.
Manufacturer Cybersecurity Solutions from BPM
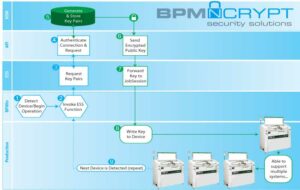 Unlike other security solutions that are expensive, rigid, and one-size-fits-all, BPM offers a range of options based on your particular needs
Unlike other security solutions that are expensive, rigid, and one-size-fits-all, BPM offers a range of options based on your particular needs
- Flexible: It can integrate with your existing security systems. Can be customized to the unique requirements of the project
- Scalable: we don’t require a separate HSM for each of our automated systems; One HSM (or secure server) can support several BPM high-speed programming systems
- Affordable: BPM does not charge per device and all of our APS is enabled to support encryption; you have an initial investment with no usage fees
Cybersecurity Solutions from BPM | Easy Engineering Interview

by Scott Bronstad | Dec 16, 2022 | Events
Here are the five competing for Mr/Ms Ugliest Sweater ’22: Ebony, Lyn, James, Stephen, and Nga
BPM celebrated Christmas with our BPM “Family” with lots of fajitas and sweets. The “Ugly Sweater” contest goes way back… this year, we’re having you vote in the comments below. Let us know who is your pick for Mr/Ms Ugly Sweater ’22. The rules are simple: the most votes win first place, and the next most votes win 2nd… voting will close at the end of the day on Monday, December 19, 2022. You can also vote on the LinkedIn poll here
House of Pies is a Houston institution of higher calories
This is a close as we get to a ‘White Christmas’ in Houston
Folks lined up for fajitas and fixin’s
The line went out the door…
Back of the line… snooze you lose…
Good thing there was lots of food…
“Chillin’ with my Gnomies”
We’re all going to need a nap this afternoon…

Programmable devices are also used in the automotive industry, such as in self-driving cars. These cars are equipped with sensors and algorithms that allow them to navigate and make decisions on the road. Some examples of programmable devices used in automotive include:


 Unlike other security solutions that are expensive, rigid, and one-size-fits-all, BPM offers a range of options based on your particular needs
Unlike other security solutions that are expensive, rigid, and one-size-fits-all, BPM offers a range of options based on your particular needs